Padding Oracle
Post from https://pentesterlab.com/****
Cipher Block Chaining
CBC is an encryption mode in which the message is split into blocks of X bytes length and each block is XORed with the previous encrypted block. The result is then encrypted.
The following schema (source: Wikipedia) explains this method: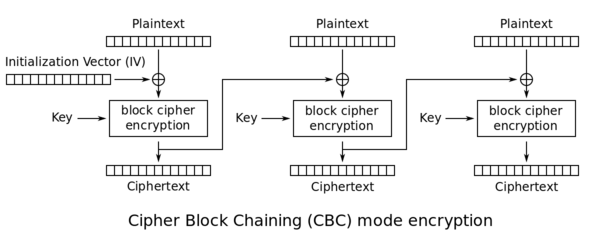
During the decryption, the reverse operation is used. The encrypted data is split in block of X bytes. Then the block is decrypted and XORed with the previous encrypted block to get the cleartext. The following schema (source: Wikipedia) highlights this behavior:
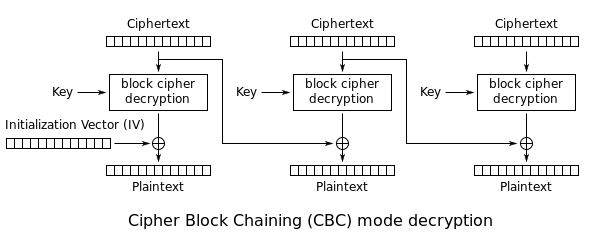
Since the first block does not have a previous block, an initialization vector (IV) is used.
Padding
As we saw, the encryption is done by blocks of fixed size. To ensure that the cleartext exactly fit in one or multiple blocks, padding is often used. Padding can be done in multiple ways. A common way is to use PKCS7. With PKCS7, the padding will be composed of the same number: the number of bytes missing. For example, if the cleartext is missing 2 bytes, the padding will be \x02\x02.
Let’s look at more examples with a 2 blocks:
| Block #0 | Block #1 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| byte #0 | byte #1 | byte #2 | byte #3 | byte #4 | byte #5 | byte #6 | byte #7 | byte #0 | byte #1 | byte #2 | byte #3 | byte #4 | byte #5 | byte #6 | byte #7 |
| ‘S’ | ‘U’ | ‘P’ | ‘E’ | ‘R’ | ‘S’ | ‘E’ | ‘C’ | ‘R’ | ‘E’ | ‘T’ | ‘1’ | ‘2’ | ‘3’ | 0x02 | 0x02 |
| ‘S’ | ‘U’ | ‘P’ | ‘E’ | ‘R’ | ‘S’ | ‘E’ | ‘C’ | ‘R’ | ‘E’ | ‘T’ | ‘1’ | ‘2’ | 0x03 | 0x03 | 0x03 |
| ‘S’ | ‘U’ | ‘P’ | ‘E’ | ‘R’ | ‘S’ | ‘E’ | ‘C’ | ‘R’ | ‘E’ | ‘T’ | 0x05 | 0x05 | 0x05 | 0x05 | 0x05 |
| ‘S’ | ‘U’ | ‘P’ | ‘E’ | ‘R’ | ‘S’ | ‘E’ | ‘C’ | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 | 0x08 |
Padding Oracle
When an application decrypts encrypted data, it will first decrypt the data; then it will remove the padding. During the cleanup of the padding, if an invalid padding triggers a detectable behaviour, you have a padding oracle vulnerability. The detectable behaviour can be an error, a lack of results, or a slower response.
If you detect this behaviour, you can decrypt the encrypted data and even encrypt any cleartext.
How to exploit
You could use https://github.com/AonCyberLabs/PadBuster to exploit this kind of vulnerability.
In order to test if the cookie of a site is vulnerable you could try:
perl ./padBuster.pl http://10.10.181.45/index.php "Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ==" 8 -encoding 0 -cookies "auth=Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ=="
Encoding 0 means that base64 is used (but others are available, check the help menu).
You could also abuse this vulnerability to encrypt new data. For example, imagine that the content of the cookie is “user=MyUsername”, then you may change it to “user=administrator” and escalate privileges inside the application. You could also do it using padusterspecifying the -plaintext parameter:
perl ./padBuster.pl http://10.10.181.45/index.php "Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ==" 8 -encoding 0 -cookies "auth=Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ==" -plaintext "user=administrator"
If the site is vulnerable padbusterwill automatically try to find when the padding error occurs, but you can also indicating the error message it using the -error parameter.
perl ./padBuster.pl http://10.10.181.45/index.php "Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ==" 8 -encoding 0 -cookies "hcon=Nl0OpaQYeGPMJeWSih2iiQ==" -error "Invalid padding"
The theory
In resume, you can start decrypting the encrypted data by guessing the correct values that can be used to create all the different paddings. Then, the padding oracle attack will start decrypting bytes from the end to the start by guessing which will be the correct value that creates a padding of 1, 2, 3, etc.
If we zoom in, we can see that the cleartext byte C15 is just a XOR between the encrypted byte E7 from the previous block, and byte I15 which came out of the block decryption step:
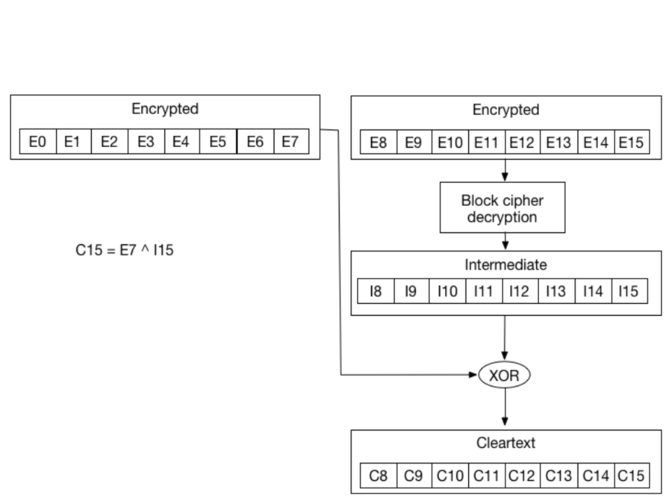
This is also valid for all other bytes:
C14 = I14 ^ E6C13 = I13 ^ E5C12 = I12 ^ E4- …
Now if we modify E7 and keep changing its value, we will keep getting an invalid padding. Since we need C15 to be \x01. However, there is one value of E7 that will give us a valid padding. Let’s call it E'7. With E'7, we get a valid padding. And since we know we get a valid padding we know that C'15 (as in C15 for E'7) is \x01.
\x01 = I15 ^ E'7
The gives us:
I15 = \x01 ^ E'7
So we are able to compute I15.
Since we know I15, we can now compute C15
C15 = E7 ^ I15 = E7 ^ \x01 ^ E'7
Now that we have C15, we can move to brute-forcing C14. First we need to compute another E7 (let’s call it E''7) that gives us C15 = \x02. We need to do that since we want the padding to be \x02\x02 now. It’s really simple to compute using the property above and by replacing the value of C15 we want (\x02) and I15 we now know:
E''7 = \x02 ^ I15
After brute force E6, to find the value that gives us a valid padding E''6, we can re-use the formula:
C14 = I14 ^ E6
to get
I14 = \x02 ^ E''6
Once we get I14, we can compute C14:
C14 = E6 ^ I14 = E6 ^ \x02 ^ E''6
Using this method, we can keep going until we get all the ciphertext decrypted.
Detection of the vulnerability
To get started, you can register an account and log in with this account (to make things easier, you get automatically logged in when you register).
If you create an account and log in two times with this account, you can see that the cookie sent by the application didn’t change.If you log in many times and always get the same cookie, there is probably something wrong in the application. The cookie sent back should be unique each time you log in. If the cookie is always the same, it will probably always be valid and there won’t be anyway to invalidate it.
Now, if you try to modify the cookie, you can see that you get an error from the application.